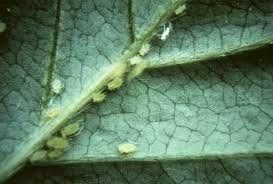
Strawberry aphids are considered one of the most damaging and widespread pests described earlier. They are extremely prolific and are able to cause significant losses to strawberry crops since they suck sap from plant tissues. More often than not the management of aphids depends on the prevention measures and control measures especially by those who prefer using strawberry aphids organic control measures.
Some Essential Info Concerning Aphids as Well as Its Effects on the Strawberry Plant
They are oval-shaped insects with soft exoskeleton usually found close-packed, often on the underside of the leaves, stems, and buds. It feeds on its host plant by inserting a slender mouth part into plant tissues and withdrawing sap which interferes with the growth of the plant by causing stunted growth and curled leaves and less fruit production. In strawberries, this feeding behaviour leads to low production, poor quality of fruits and higher tendency to bacterial and fungal diseases. Also, aphids produce a sweet substance called honeydew on which ants can feed but which can also give rise to the sooty mold fungi.
Currently the foremost important is the strawberry aphid (Chaetosiphon fragaefolii) that is common in temperate regions. This species is particularly vicious as it spreads viral diseases such as the strawberry crinkle that may cause the total loss of crop yields if not intercepted.
Prevention Techniques
Aphids can prove to be a very destructive pest that attacks and badly affects the strawberry plant. It is possible to minimize the aphid incidence by adopting some cultural practices.
- Proper Plant Spacing:
Receipt of ohed space increases the rate of reproduction and thereby enhances the population density of aphids. Spacing out the plants also ensures free air flow and thus diminishes the favorite grounds of aphids to stay. When planting your strawberries, it is wise to space them in such a way that you do not provide the ideal conditions these aphids would like.
- Companion Planting:
One can look at getting companion plants such as garlic, chives, or marigolds which can help to reduce the attractiveness of the area to the aphids. There are plants that produce chemicals which enable them to repel aphids from your strawberries. Companion planting also attracts desirable pests such as ladybugs and lacewings because these are natural enemies of aphids.
- Pruning and Mulching:
Pruning of the strawberry plants is best practised to minimize the hiding places of the aphids while mulching leads to conservation of moisture hence the growth of the plants. Aneat mulch applied around the plants can keep aphids from attacking the plants by making it difficult for them to get to the plants.
Biological control of the pest with the help of Beauveria bassiana
Biological control agents act as a good tool to organic farmers and gardeners since they reduce use of chemical insecticides. Among all the other agents, Beauveria bassiana pesticide is recognized as one of the most effective agents for aphid control because it is the fungal entomopathogen that infects and kills aphids as well as other tender-skinned insects.
BEAUVERIA BASSIANA is active in BEVERIA WP which is a bio pesticide by contact that has the ability to infest the aphids with fungal spores. It attaches itself on the outer skin of an aphid and burrows into the skin which leads to the death of the insect after 24 to 48 hours. A good thing with this strategy of control is that it does not pose harm to the environment, the other beneficial insects and pollinators.
Using beauveria bassiana biological control agent offers several advantages:Using Beauveria bassiana offers several advantages:
- Targeted Action: The fungus is lethal to aphids but non-toxically affects other insects or plants or the environment in which the aphids are found.
- Sustainability: Organoaek Beauveria bassiana is an endophytic fungi, which means that it does not need to be applied artificially; it is a natural product hence can be used in an organic farm.
- Reduced Chemical Dependence: It reduces the use of chemical insecticides therefore helping in the enhancement of a good environment.
Application of BEVERIA WP
When using BEVERIA WP, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for application. Typically, the product is applied as a foliar spray, covering the leaves where aphids are most likely to be found. Regular applications every 7 to 10 days ensure that the fungal spores remain active and can continue to infect aphids as they come into contact with the treated surfaces.
For best results, BEVERIA WP should be applied during the early stages of an infestation. Mixing 0.5 to 1.0 grams of the product per liter of water and applying it evenly over the plants helps ensure thorough coverage. Reapplication is necessary to maintain control as the aphid population is gradually reduced.
Nevertheless, BEVERIA WP can be applied in pest management programmes or integrated pest management (IPM) for other pests including whiteflies and spider mites. When you apply this particular species of insects into your gardening practice, you will have saved your strawberries from the effect of the aphids simultaneously contributing to a healthier garden.
Conclusion
Aphids in strawberry cropping hence can be managed effectively through an effective prevention and control measure. It’s also important to practice crowding control, intercropping, and pruning, so as to minimize the threat posed by aphids. Those who are in search of an organic approach can use biological control agents such as Beauveria bassiana and are efficient in treating the infestation.
When employed in the pest control programs, BEVERIA WP eliminates the impact of aphids on strawberries without the use of chemical pesticides. It increases your yield and the quality of your fruits and besides, these practices conserve useful insects and improve the health of the soil.